
The global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) has encountered a significant roadblock — the price tag. According to a survey conducted by S&P Global Mobility, nearly half of the 7,500 respondents worldwide cited high EV prices as the leading barrier to adoption.
Despite a notable drop in average EV prices over the last year, consumer interest has waned, revealing a complex interplay of factors influencing the global EV market.
Survey Says: Price Tops the List of Reasons People Avoid EVs (PDF)
Price Fatigue and Consumer Sentiment
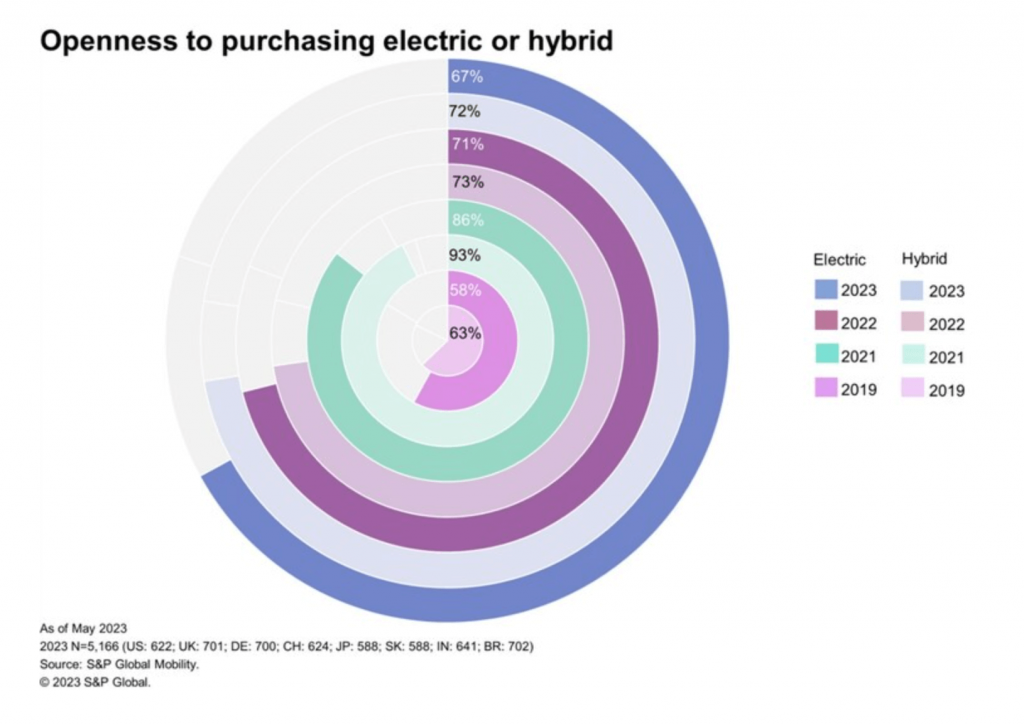
The survey exposes a sharp decline in consumer enthusiasm for EVs, with about two-thirds of respondents expressing openness to purchasing an EV—a significant drop from 2021. Yanina Mills, Senior Technical Research Analyst at S&P Global Mobility, attributes this shift to “price fatigue,” driven by rising interest rates and inventory shortages.
Even with a broader selection of EV models now available, including SUVs, crossovers, pickups, and luxury sedans, automakers’ delays in producing lower-priced models have hindered widespread adoption.
While many of these models make economic sense compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, consumers struggle to navigate the complex landscape of the total cost of ownership, including tax credits, incentives, installation expenses, energy costs, and more.
Charging Concerns and Range Anxiety
While price remains the top concern, charging issues closely follow in the hierarchy of barriers to EV adoption. Approximately half of respondents express concerns about the time required for charging, and over 40% worry about the availability of charging stations. These concerns have shifted from 2021, indicating a changing landscape of consumer priorities.
Consumers are willing to spend 30 to 60 minutes charging at a public station, but the charging infrastructure must align with these expectations. Fast charging networks, such as Tesla’s NACS design, are crucial for meeting consumer demands.
Additionally, high-capacity built-in chargers in EVs contribute to faster charging times, with some models capable of an 18-minute charge from 10% to 80%.
Home Charging Realities
Dispelling the notion that charging challenges predominantly affect those without home charging facilities, the survey findings present a different narrative.
Although respondents acknowledge that charging at home is the most prevalent and preferred method, a mere 42% of EV owners routinely charge their vehicles at home.
This contradicts the industry’s prevailing assumption that a majority of owners would opt for home recharging.
Range Preferences and Technology Expectations
Consumer preferences for the EV range align with current market offerings, with most respondents willing to accept a range below 300 miles.
The survey indicates that current EV technology is ready for acceptance, but consumers are holding back, waiting for the next technological advance. Sixty-two percent of respondents express a reluctance to purchase until vehicle technology improves.
Conclusion
The global EV market faces a formidable obstacle—the price barrier. As consumers grapple with the total cost of ownership and intricate charging considerations, the industry must address these concerns to drive widespread adoption.
Beyond engineering advancements, understanding and mitigating the financial aspects that lead to consumer resistance will be pivotal in steering the electric vehicle revolution toward a more sustainable future.



