Automobile sales are a cornerstone of the U.S. economy, exerting substantial influence across various sectors, boosting consumer expenditure, and generating considerable tax revenue. This article explores the diverse impacts of the auto industry, detailing its contributions to GDP, employment, manufacturing, and consumer spending behavior.
The Role of Automobile Sales in the U.S. Economy (PDF)
Economic Contribution of the Automobile Industry
The automotive sector contributes significantly to the U.S. economy, playing a pivotal role in economic stability and growth.
GDP Contribution
The automobile industry is a key component of the U.S. economy, contributing about 3% to the nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This contribution comes from vehicle sales, services, and the broader automotive ecosystem, which includes parts suppliers and dealership payrolls.
Tax Revenue
Car sales generate nearly $280 billion annually in federal, state, and local taxes. This substantial tax revenue supports various public services and infrastructure projects, highlighting the automotive sector’s importance beyond just the commercial sphere.
Employment in the Automobile Industry
The automotive industry is a major employer in the U.S., providing jobs across a range of sectors.
Job Creation
The industry supports approximately 9.7 million jobs, translating to about 5% of all private-sector employment. These jobs are not confined to manufacturing; they span sales, finance, insurance, and transportation services, reflecting the industry’s broad economic footprint.
| Sector | Employment (millions) |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 2.5 |
| Sales | 1.5 |
| Finance & Insurance | 1.2 |
| Transportation | 1.0 |
| Other Services | 3.5 |
| Total | 9.7 |
Sales and Market Dynamics

Historical Sales Trends
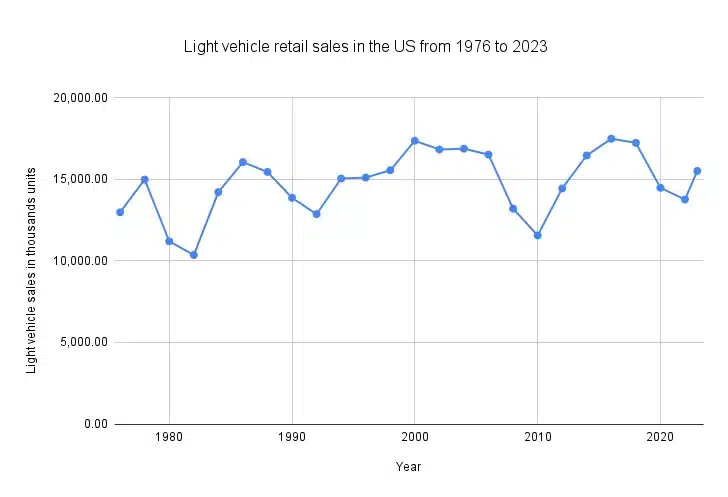
Light vehicle sales in the U.S. have fluctuated over the decades. Notable declines occurred during economic downturns such as the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the industry has demonstrated resilience with robust recoveries following these periods.
For instance, in 2023, auto sales reached around 15.5 million units. Trucks dominated the market, comprising about 79.24% of all auto sales in early 2023.
Impact of COVID-19
The pandemic led to a sharp decline in auto sales and production in early 2020. Sales dropped from an annual rate of 17 million units in February 2020 to 8.6 million in April 2020. However, by late 2020, the industry saw a V-shaped recovery, driven by a shift in consumer demand from services to goods. Supply chain disruptions, especially semiconductor shortages, have continued to impact production, leading to increased prices for used cars due to the scarcity of new vehicles.
Manufacturing and Export

Manufacturing Statistics
- The auto industry is the largest manufacturing employer in the U.S., emphasizing its importance in the industrial sector.
- It is also the largest exporter, with nearly $97 billion worth of cars and parts exported annually.
Consumer Spending
Automobile sales are a major driver of consumer spending, which is a vital component of the U.S. economy.
Economic Mobility
Car sales enable economic mobility by allowing individuals to access jobs, education, healthcare, and other essential services (Autos Innovate). This, in turn, fosters broader economic participation and growth.
Spending Insights
In early 2023, the average transaction price for new vehicles in the U.S. stood at $48,763, while electric vehicles averaged a higher price of $58,385. Despite a slight reduction in these transaction prices, the elevated costs of financing remain a significant hurdle for many prospective car buyers.
Conclusion
The automobile industry is integral to the U.S. economy, affecting GDP, employment, manufacturing, and consumer spending. Its resilience and adaptability are evident in its recovery from economic fluctuations, including the recent challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. As the industry continues to innovate, especially in electric vehicles, its economic impact is set to grow even further.
Understanding the comprehensive role of the automobile industry helps in appreciating its significance and fostering its sustained growth and development. The automotive sector is not just about cars; it is a driving force behind economic prosperity and a pillar of modern society.



